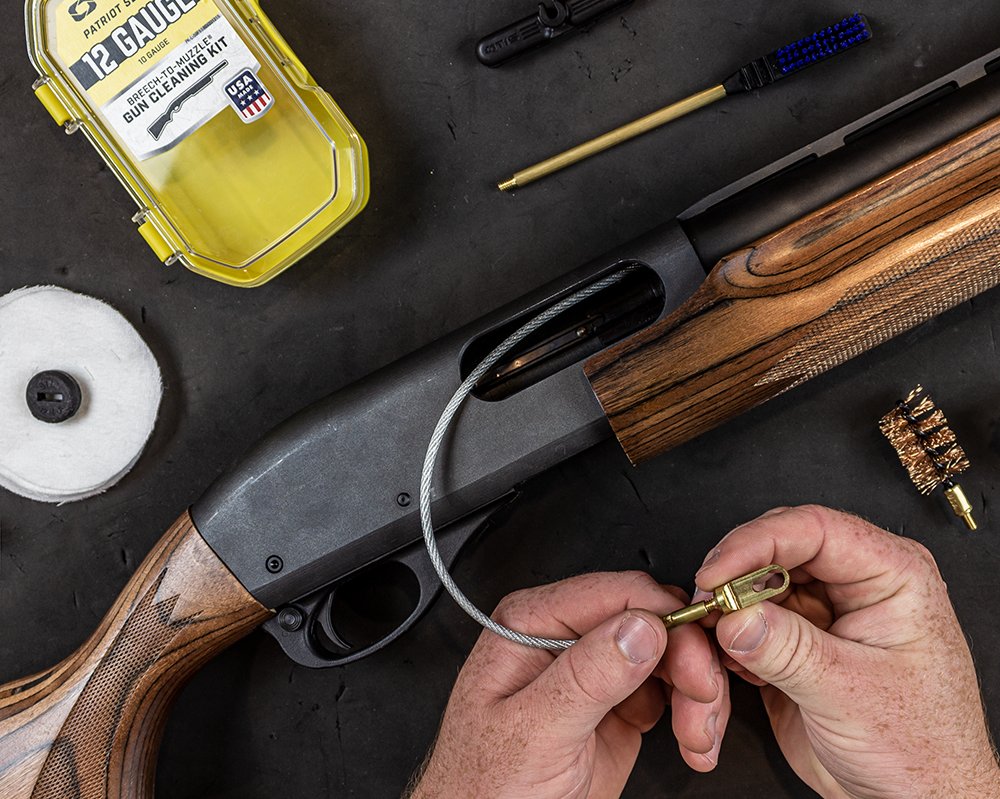

Cleaning kits for shotgun
Shotguns, like any mechanical device, demand regular care for optimal functioning.
Jul 24, 2024 | by N Johansson

Survival is a fundamental aspect of life, encompassing the essential actions and strategies necessary to continue living in adverse conditions. It transcends physical and mental boundaries, involving everything from basic human needs to complex psychological resilience. Survival can be contextualized in various environments such as the wilderness, urban settings, extreme climates, and even during natural disasters.
Understanding survival mechanisms is crucial for preparedness and resilience. By grasping the fundamental principles of survival, individuals can enhance their ability to react appropriately in life-threatening situations. This knowledge not only increases the chances of survival but also reduces the panic and fear often associated with such circumstances.
Survival refers to the ability to remain alive and functional under conditions that threaten life. This encompasses obtaining essential resources like food, water, and shelter, as well as maintaining physical and mental health. The scope of survival extends from immediate, short-term crises to prolonged, sustained living in harsh environments.
Historically, survival instincts have been a crucial aspect of human evolution. Early humans developed survival skills out of necessity, learning to hunt, gather, and protect themselves from predators and natural threats. These instincts have been honed over millennia, forming the basis of our inherent survival strategies.
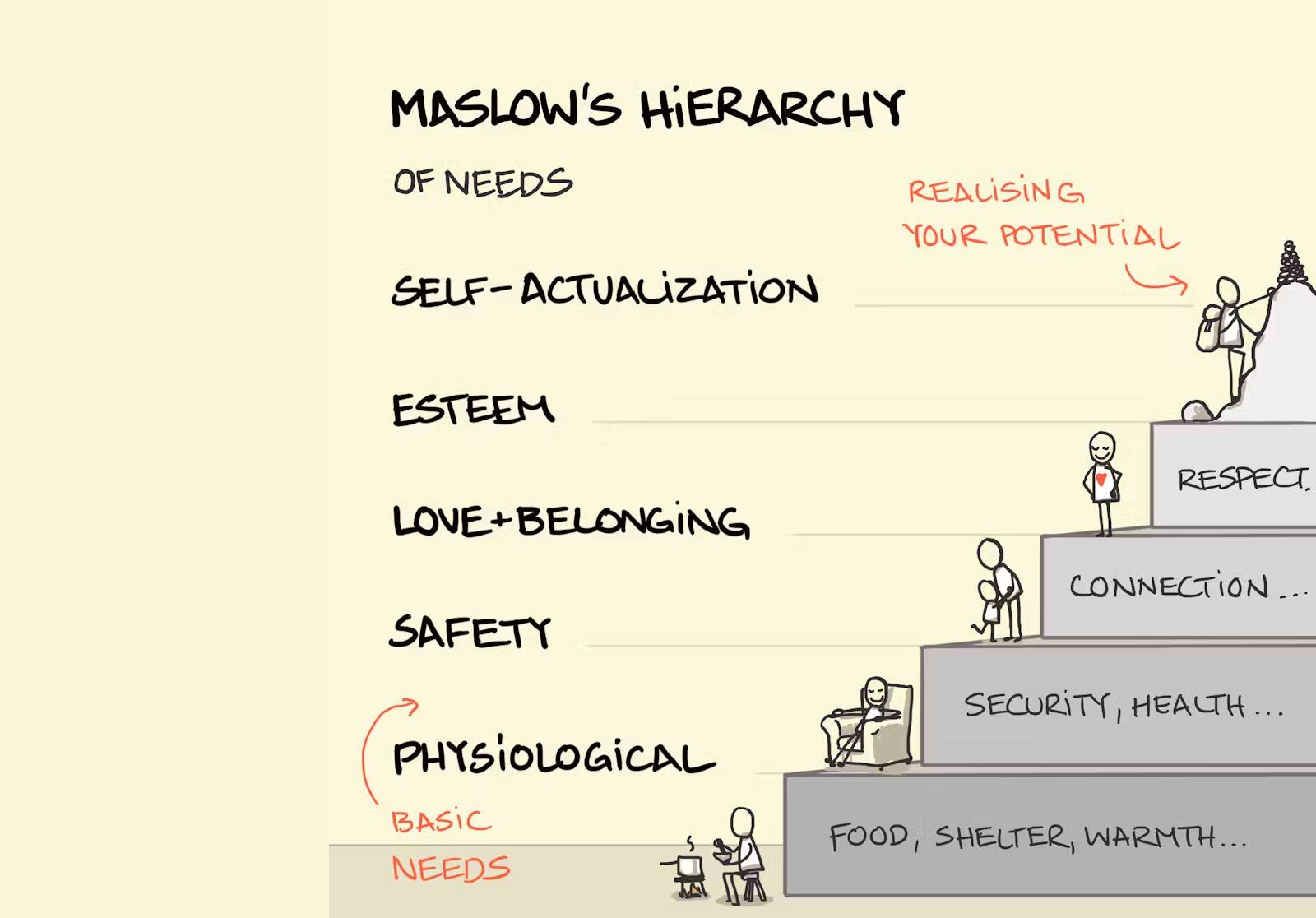
The basic needs for survival include food, water, shelter, and warmth. Securing these essentials is the first step in any survival situation. Understanding how to find and prepare food, locate and purify water, build or find shelter, and maintain body temperature can significantly enhance survival prospects.
Water is the most critical element for survival. The human body is composed of about 60% water, and it plays a vital role in maintaining bodily functions.
Survival time without water: On average, a person can survive without water for about 3 days, although this can vary depending on environmental conditions, activity level, and individual health. Dehydration can lead to serious health issues, including kidney failure and shock, and can be fatal if not addressed promptly.
Finding and purifying water: In a survival situation, it's crucial to locate a water source. Natural sources such as rivers, streams, and lakes can be viable options. However, water from natural sources should be purified before consumption to avoid waterborne diseases. Purification methods include boiling, using water purification tablets, and filtering through commercial water filters.
Food provides the energy and nutrients needed to maintain bodily functions and physical strength.
Survival time without food: A person can survive without food for about 3 weeks, but this duration can vary based on individual health, hydration levels, and environmental factors. Starvation can lead to muscle loss, weakened immune function, and eventually death.
Finding and preparing food: In the wild, food can be sourced from foraging plants, hunting animals, and fishing. Knowledge of edible plants and animals is crucial to avoid poisoning. In an urban environment, stockpiling non-perishable food items such as canned goods, dried fruits, and nuts is essential. Cooking food, when possible, helps to kill harmful pathogens and parasites.
Shelter provides protection from environmental hazards such as extreme weather, predators, and insects.
Survival time without shelter: The need for shelter can be immediate, especially in harsh weather conditions. Exposure to extreme temperatures can lead to hypothermia or heatstroke within hours. Shelter is essential for maintaining body temperature and protecting against the elements.
Building or finding shelter: In the wilderness, shelters can be constructed using natural materials like branches, leaves, and snow. Techniques include building lean-tos, debris huts, or snow caves. In an urban setting, seeking out sturdy buildings, basements, or temporary structures can provide necessary protection.
Maintaining body temperature is vital for survival, particularly in cold environments.
Survival time without warmth: In cold conditions, hypothermia can set in within minutes to hours, depending on the severity of the weather and the individual's clothing and physical condition. Hypothermia occurs when the body loses heat faster than it can produce it, leading to a dangerous drop in core body temperature.
Maintaining warmth: Techniques to maintain warmth include layering clothing, using thermal blankets, and building fires. In cold climates, insulating shelters with materials like leaves or snow can help retain heat. Knowing how to start a fire using various methods (e.g., friction, flint and steel, or matches) is an essential survival skill.
Understanding and prioritizing these basic needs can significantly enhance one's chances of survival in any situation. Proper preparation, knowledge, and skills are key to securing food, water, shelter, and warmth effectively.
Wilderness survival requires specific skills and tools. Key skills include fire-making, navigation, foraging, and hunting. Essential tools might include a knife, fire starter, compass, and a first aid kit. Knowledge of the local environment and its resources is also crucial.
Urban survival involves different challenges compared to wilderness survival. Key considerations include finding safe shelter, securing food and water in an urban environment, and navigating potentially dangerous situations. Strategies might include building a network of trusted contacts, understanding the layout of the city, and having a plan for evacuation or sheltering in place.

Shotguns, like any mechanical device, demand regular care for optimal functioning.
Mental toughness is a critical component of survival. It involves the ability to stay focused, determined, and resilient in the face of adversity. This mindset helps individuals overcome fear, manage stress, and maintain a positive outlook, which are all essential for long-term survival.
Effective coping mechanisms and stress management techniques can greatly improve one’s ability to survive. Techniques such as mindfulness, deep breathing exercises, and maintaining a routine can help manage stress levels and prevent panic.
Real-life stories of resilience and survival provide valuable lessons and inspiration. Accounts of individuals who have survived extreme conditions by using their mental and emotional strength highlight the importance of resilience and a positive attitude.
Survival strategies vary greatly depending on the environment. Understanding the specific challenges and resources of different environments—whether wilderness, urban, or extreme climates—is crucial for effective survival planning and adaptation.
Adaptation strategies include learning to use available resources, modifying shelter and clothing to suit the environment, and developing new skills as needed. Flexibility and resourcefulness are key to adapting successfully.
Situational awareness involves being aware of your surroundings and understanding the potential threats and opportunities they present. This awareness helps in making informed decisions and responding effectively to changing conditions.
Basic first aid and medical knowledge are essential for survival. Understanding how to treat injuries, manage illnesses, and use medical supplies can prevent minor issues from becoming life-threatening.
Preventive measures include maintaining good hygiene, being cautious of potential hazards, and staying physically fit. Preventing injuries and illnesses is always preferable to treating them after they occur.
Regular health check-ups help identify and address potential health issues before they become serious. Staying aware of your health status and managing chronic conditions are important aspects of survival.
A well-prepared survival kit includes items such as food, water, a first aid kit, a knife, fire-starting tools, and a means of communication. These essentials can help address basic needs in an emergency.
Survival kits should be customized based on the specific environment and potential scenarios. For example, a wilderness survival kit might include navigation tools, while an urban kit might prioritize items like masks and gloves.
Regularly checking and updating the survival kit ensures that all items are in good condition and up to date. This includes replacing expired food and medicine, checking batteries, and ensuring the kit is tailored to current needs.
Continuous learning and skill development are vital for effective survival. Staying informed about new survival techniques and technologies can enhance preparedness.
Participating in survival courses and obtaining certifications can provide valuable hands-on experience and knowledge. These courses cover a wide range of topics from basic survival skills to advanced medical training.
Online resources, such as survival blogs, forums, and videos, offer a wealth of information. Joining community groups can also provide support, shared knowledge, and opportunities for group training.
A strong support network can significantly enhance survival chances. This includes family, friends, and community members who can provide assistance, resources, and emotional support.
Communities play a crucial role in survival, especially in large-scale emergencies. Community preparedness programs, shared resources, and coordinated efforts can improve overall resilience.
While some survival situations may require independent action, collaboration often provides greater resources and support. Working with others can enhance problem-solving and reduce the individual burden.
Technological advancements have provided a range of tools and gadgets that can aid survival. These include GPS devices, solar chargers, portable water filters, and emergency communication devices.
Technology can greatly enhance survival chances by providing accurate information, facilitating communication, and offering practical solutions to common survival challenges.
Despite its benefits, technology also has limitations. Devices can fail, batteries can deplete, and signals can be lost. It’s important to have non-technological backup plans and skills.
Understanding the psychological aspects of survival can help individuals prepare mentally for the challenges they may face. This includes recognizing common emotional responses and developing strategies to cope with them.
Fear and panic are natural responses to life-threatening situations, but they can be detrimental to survival. Techniques such as deep breathing, staying focused on tasks, and maintaining a positive mindset can help overcome these responses.
A positive mindset can significantly impact survival outcomes. It fosters resilience, encourages proactive problem-solving, and helps maintain physical and mental health.
Examining famous survival stories provides valuable insights into effective survival strategies and the human capacity for resilience. Stories like those of Aron Ralston and the Andes plane crash survivors offer practical lessons and inspiration.
Analyzing real-life survival situations helps identify common challenges and successful strategies. These lessons can inform personal survival plans and improve preparedness.
A detailed analysis of the tactics used in successful survival stories can reveal important principles and techniques. This includes understanding decision-making processes, resource management, and adaptability.
Natural disasters come in various forms, including earthquakes, floods, hurricanes, and wildfires. Each type presents unique risks and requires specific preparation strategies.
An emergency plan outlines the actions to take before, during, and after a disaster. It includes evacuation routes, communication plans, and emergency contacts.
Participating in community preparedness programs enhances overall resilience. These programs offer training, resources, and coordinated response efforts to help communities withstand and recover from disasters.
Financial stability is an often-overlooked aspect of survival. Having financial resources can provide access to essential supplies, medical care, and recovery efforts.
Managing finances during crises involves having an emergency fund, reducing unnecessary expenses, and planning for potential income disruptions. It’s important to have a financial plan in place for emergencies.
An emergency fund provides a financial safety net during crises. Saving regularly and ensuring the fund is easily accessible can help manage unexpected expenses and emergencies.
Survival requires a combination of physical skills, mental resilience, and preparedness. Understanding survival mechanisms, adapting to the environment, and maintaining health and safety are crucial.
The essence of survival lies in the ability to remain calm, resourceful, and
Articles you might also like: